Shear-Induced Desorption in Polymer Brushes
D. L. Anastassopoulos, N. Spiliopoulos, A. A. Vradis, C. Toprakcioglu, S. M. Baker, and A. Menelle.
Macromolecules 2006, 39, pp. 8901-8904.
In this
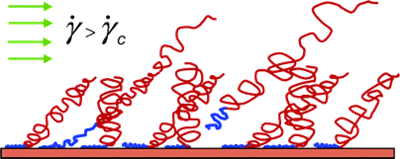
study, we have used neutron reflectometry to study end-adsorbed polystyrene
brushes exposed to shear flow in good solvent. The brush volume fraction
profiles show no evidence of change with increasing ![]() below a shear rate threshold which
is found to depend on the brush interchain spacing (or equivalently, the mean
blob size) and is shown to increase with s-3 (or ξ-3). A discontinuous
transition in desorption rate is observed when
below a shear rate threshold which
is found to depend on the brush interchain spacing (or equivalently, the mean
blob size) and is shown to increase with s-3 (or ξ-3). A discontinuous
transition in desorption rate is observed when ![]() =
=![]() (corresponding to a critical Weissenberg number Wc < 0.5) with a rapid and
sharp reduction in adsorbance for
(corresponding to a critical Weissenberg number Wc < 0.5) with a rapid and
sharp reduction in adsorbance for ![]() >
> ![]() The
absence of any observable change in the volume fraction profile just before the
onset of desorption suggests that the desorption process is probably mediated
by only a small fraction of strongly extended chains dragged by the shear flow.
The results may have important implications in colloidal stability and
lubrication since the findings demonstrate the existence of a limiting shear
rate above which substrates are rapidly stripped of their protective layer of
adsorbed polymer. Furthermore, the quantitative relationship we have
established between brush structure and brush susceptibility to shear flow for
end-adsorbed polymers may be of predictive value in determining or even tuning
the response of a brush to a given shear flow regime.
The
absence of any observable change in the volume fraction profile just before the
onset of desorption suggests that the desorption process is probably mediated
by only a small fraction of strongly extended chains dragged by the shear flow.
The results may have important implications in colloidal stability and
lubrication since the findings demonstrate the existence of a limiting shear
rate above which substrates are rapidly stripped of their protective layer of
adsorbed polymer. Furthermore, the quantitative relationship we have
established between brush structure and brush susceptibility to shear flow for
end-adsorbed polymers may be of predictive value in determining or even tuning
the response of a brush to a given shear flow regime.